如何调查CPU是否在空等待
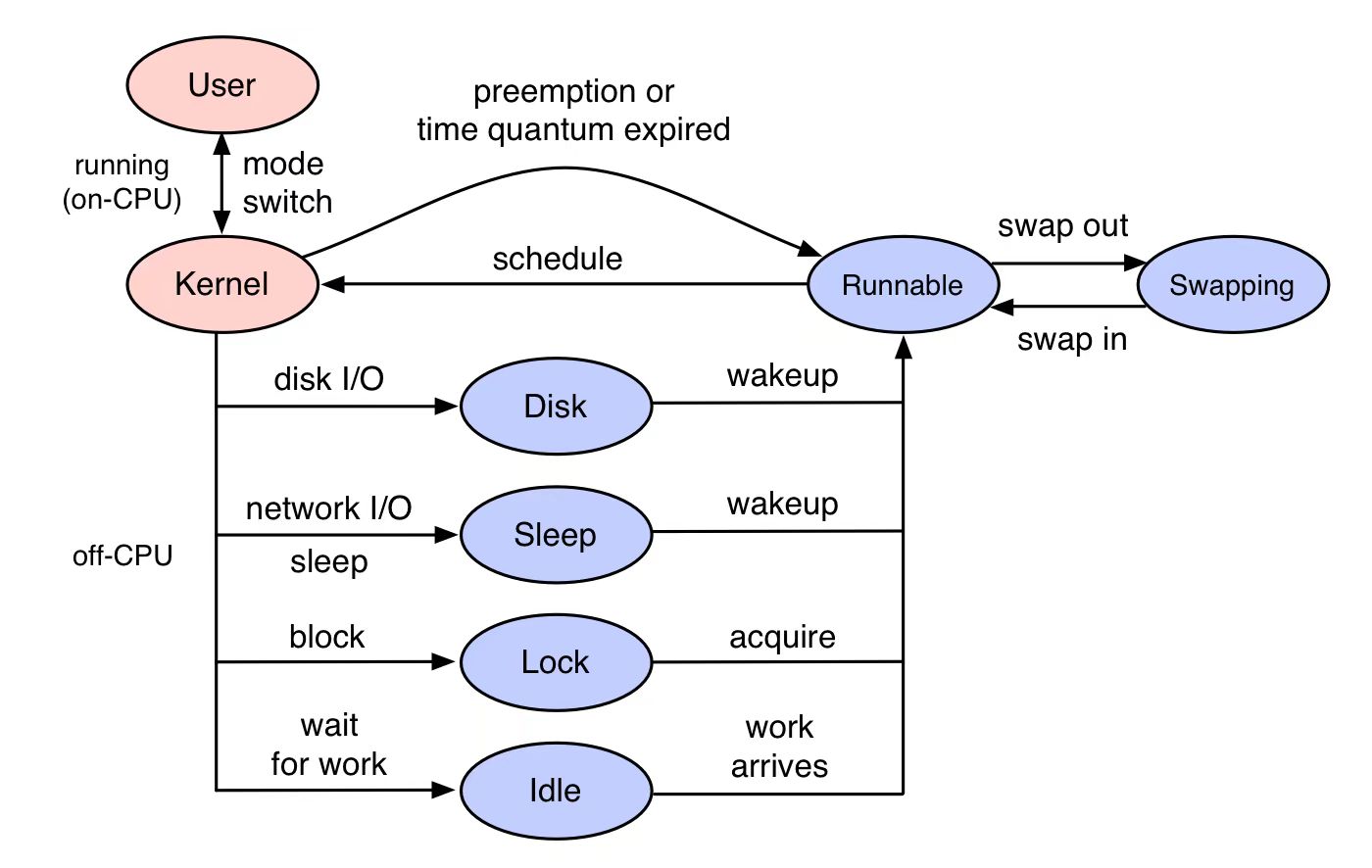
基础检查
最简单的可使用下列脚本直接看结果。
#!/bin/bash
# 检查是否安装了 iostat
if ! command -v iostat &> /dev/null
then
echo "iostat 未安装,请先安装 sysstat 包。"
exit 1
fi
# 获取 CPU 使用率和负载信息
iostat_output=$(iostat -c -d 1 2)
cpu_idle=$(echo "$iostat_output" | awk 'NR==7 {print $6}')
cpu_iowait=$(echo "$iostat_output" | awk 'NR==7 {print $4}')
load_average=$(uptime | awk -F'load average:' '{ print $2 }' | cut -d, -f1 | tr -d ' ')
# 设定阈值
idle_threshold=30.0
iowait_threshold=10.0
load_threshold=1.0
# 判断 CPU 状态
if (( $(echo "$cpu_idle > $idle_threshold" | bc -l) )); then
echo "CPU 大部分时间在空转。"
elif (( $(echo "$cpu_iowait > $iowait_threshold" | bc -l) )); then
echo "CPU 高 I/O 等待,可能有磁盘或网络瓶颈。"
elif (( $(echo "$load_average > $load_threshold" | bc -l) )); then
echo "CPU 负载高,可能�有 CPU 密集型任务。"
else
echo "CPU 负载和使用率正常。"
fi
或者是使用 BPF 工具:
offcputime-bpfcc -df -p pgrep -nx a.out 30 > out.stacks
可尝试使用
offcputime-bpfcc -df -p pgrep -nx a.out 30 > out.stacks
这条命令使用 offcputime-bpfcc 工具来分析指定进程在 off-CPU(非运行态)时的时间分布,具体做了以下事情:
-
offcputime-bpfcc: 这是一个 BPF (Berkeley Packet Filter) 工具,用于捕获进程在 off-CPU 时的堆栈跟踪。 -
-d: 打印详细的堆栈信息。 -
-f: 以格式化的方式输出堆栈信息,便于分析。 -
-p $(pgrep -nx a.out): 指定要分析的进程 ID。这里使用pgrep -nx a.out来获取名为a.out的进程的最新进程 ID。 -
30: 运行时间,表示收集数据持续 30 秒。 -
> out.stacks: 将输出内容重定向到out.stacks文件中。
这个命令的目的是分析 a.out 进程在 off-CPU 时的行为,帮助找出可能的性能瓶颈,例如 I/O 等待、锁竞争等。收集的数据会被保存到 out.stacks 文件中以供后续分析。
硬盘 io 测试
# Linux
# 写测试
dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/your_disk/testfile bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct
# 读测试
dd if=/mnt/your_disk/testfile of=/dev/null bs=1G count=1 iflag=direct
# 删除测试文件
rm -f /mnt/your_disk/testfile
#########################
# Windows
# 写测试
Write-Host "Writing test file..."
$testFile = "D:\testfile"
$buffer = New-Object Byte[] (1MB)
[IO.File]::WriteAllBytes($testFile, $buffer)
# 读测试
Write-Host "Reading test file..."
$buffer = [IO.File]::ReadAllBytes($testFile)
# 删除测试文件
Remove-Item $testFile